Pass Word
July 18, 2024•241 words
Security Best Practices and Password Hygiene
1. Password Management Basics
1.1 Remembering Two Key Passwords
- Physical Machine Password: The password to turn on and access your physical machine.
- Password Vault Password: The password to access your password manager or vault.
2. Password Hygiene Best Practices
2.1 Use Strong, Unique Passwords
- Every password should be different for each service, account, or device.
- Use a password manager to generate and store these passwords securely.
- Avoid knowing the individual passwords; let the password manager handle them.
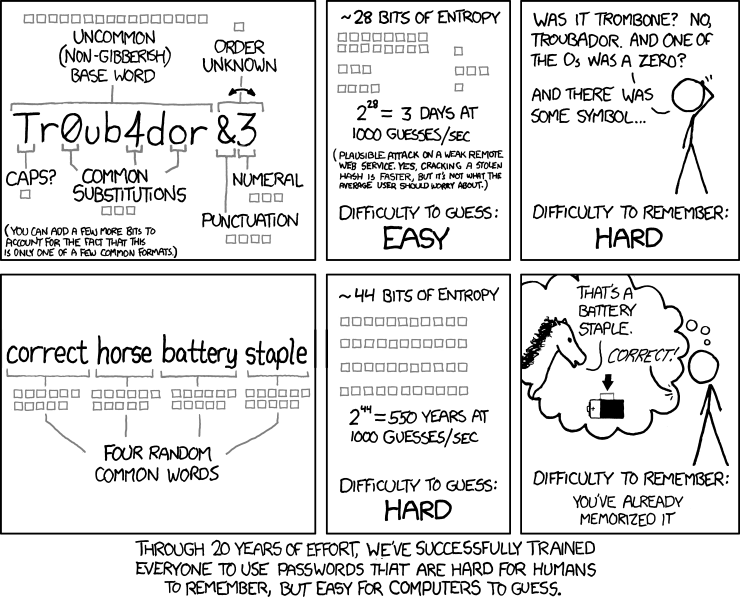
2.2 Emphasis on Length Over Complexity
- Passwords should be longer than 12 characters.
- For added strength, make them longer rather than more complex.
- Example: Generate passphrases with 4 or more random words separated by underscores (e.g.,
correct_horse_battery_staple).
3. Password Manager Usage
3.1 Generating and Storing Passwords
- Use the password manager’s generator to create random passphrases.
- Store all passwords within the password manager to ensure security and accessibility.
3.2 Auto-Fill and Integration
- Configure the password manager to auto-fill credentials in login forms.
- Ensure it integrates with browsers and other applications seamlessly.
4. Addressing Common Password Requirements
- 4.1 Dealing with Uppercase and Number Requirements
- While adding uppercase letters or numbers may be required, it does less to strengthen the password than simply adding more length.
- Follow site-specific requirements but prioritize longer passwords when possible.